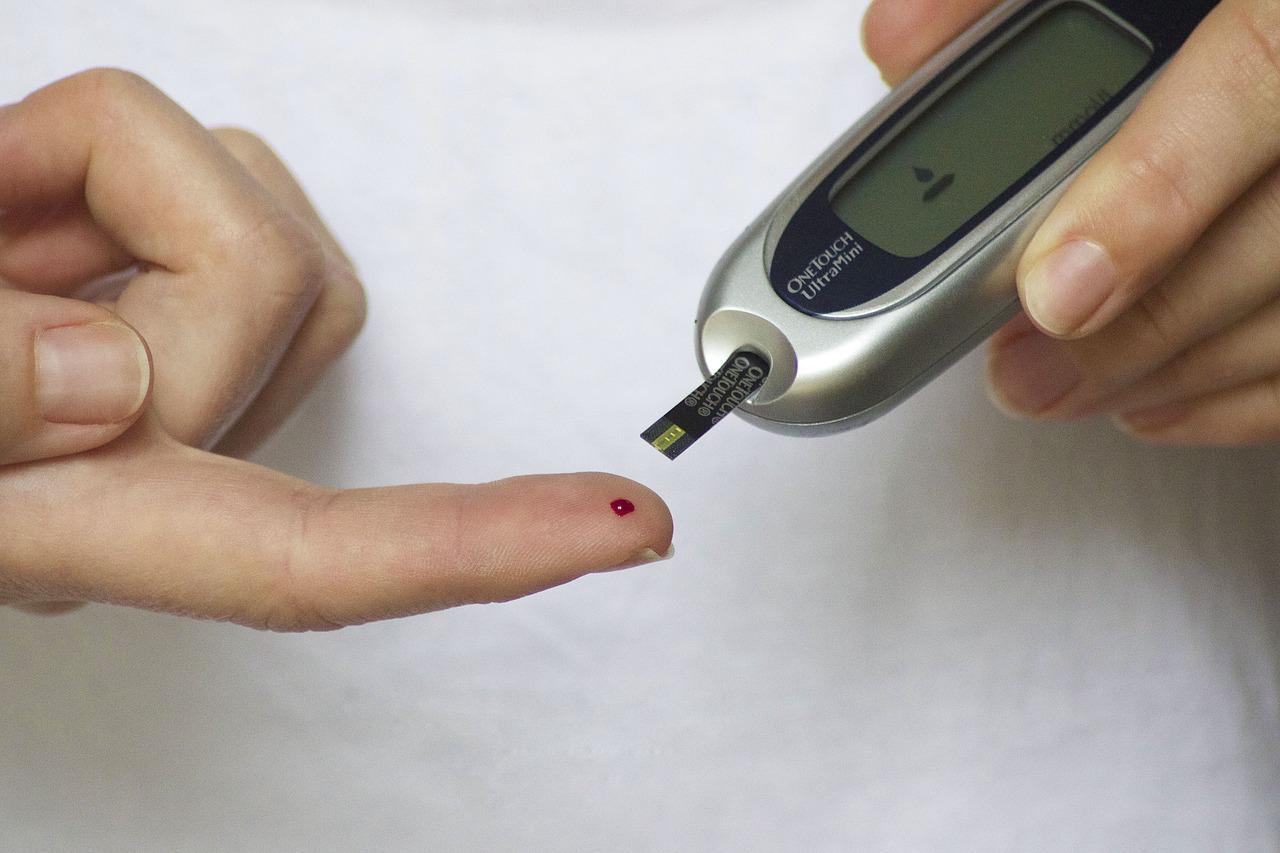
To effectively manage diabetes, it is necessary to follow prescribed medication and insulin instructions, monitor your blood glucose at home, and keep regular appointments with health care providers. Your healthcare provider will also order certain laboratory tests. Blood glucose level monitoring will help you control your diabetes and make the best food and exercise choices. You should also make frequent adjustments to your insulin as needed. However, managing diabetes is more difficult than you may think. You should not despair; it’s possible to live with diabetes.
Type 1 diabetes causes sudden symptoms
If you suspect you may have Type 1 diabetes, it is important to seek medical care as soon as possible. If left untreated, the disease can lead to complications including kidney and nerve damage. In severe cases, the condition can even cause heart disease and osteoporosis. Working with an endocrinologist can help you avoid these complications and maintain good overall health. If you suspect that you may have this disease, here are a few of the warning signs you should be aware of.
Type 2 diabetes causes insulin resistance
Insulin resistance is a common symptom of type 2 diabetes. Inflammation of the pancreas and failure of the insulin-producing cells are a major cause of diabetes. Insulin stimulates the release of stored blood sugar, which provides energy for the body. But when the amount of insulin released by the pancreas is too low, the body begins to respond poorly to it. Eventually, the b-cells begin to fail, and the blood sugar levels become too high.
Type 3 diabetes causes hyperglycemia
Although there is a general consensus that hyperglycemia is a symptom of diabetes, the condition is often asymptomatic in early stages. The condition may be detected during routine testing, or may be present without symptoms. Initial symptoms of diabetes may be a result of diabetic complications, or they may indicate the presence of the disease for some time. Hyperosmolar hyperglycemia may also occur during times of stress or if glucose metabolism is impaired.
Complications of diabetes
In addition to the risks mentioned above, people with diabetes may experience complications in the form of foot ulcers, kidney failure, nephropathy, retinopathy, and cardiovascular disease. Fortunately, these complications are often preventable, if diagnosed and managed properly. This article will describe some of the most common and serious complications of diabetes and provide recommendations for how to prevent them. Listed below are some of the most common long-term complications of diabetes. Read more here athomewithelisabeth.com
Treatment for diabetes
There are several types of treatment for diabetes. Treatment for diabetes may include insulin-sensitizing drugs, or insulin-suppressing medications. In addition to these drugs, patients can also benefit from oral medications. This article will explore the different types of diabetes treatment and discuss which might be best for you. In general, the first step is a consultation with a physician. In addition to this, it’s important to follow a strict diet plan that’s rich in fruits and vegetables.